EPTbased Second Level Address Translation (the abbreviations R, W, X... Download Scientific

Second Level Address Translation Benefits in HyperV R2
Minimum: 1.4 GHz 64-bit processor Compatible with x64 instruction set Supports NX and DEP Supports CMPXCHG16b, LAHF/SAHF, and PrefetchW Supports Second Level Address Translation (EPT or NPT) 1 Is there anyway to find out if say if an. HP Workstation xw6200 - Intel E7525 chipset, or a; DELL PowerEdge R710 2 x 2.53Ghz E5540

Is Supports Second Level Address Translation (EPT or NPT) required to use HyperV? YouTube
Second-level address translation (SLAT) is a hardware virtualization technology that reduces hypervisor overhead. To do so, SLAT addresses the inefficiencies associated with looking up virtualized memory addresses in software shadow volumes.
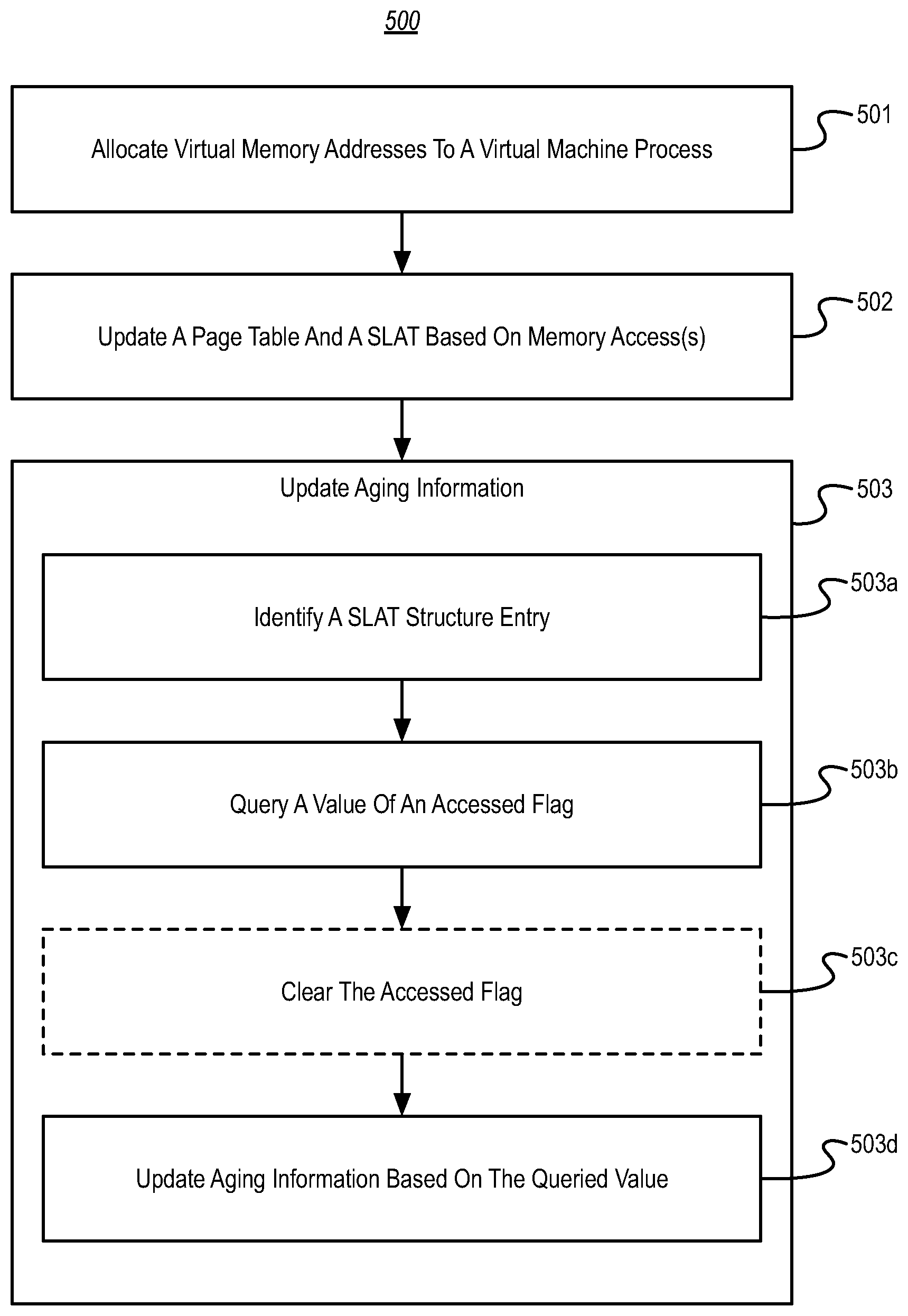
Updating aging information using secondlevel address translation for virtual addressbacked
With respect to memory management, Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V supports a new feature named Second Level Address Translation (SLAT). SLAT leverages AMD-V Rapid Virtualization Indexing (RVI) and Intel VT Extended Page Tables (NPT) technology to reduce the overhead incurred during virtual to physical address mapping performed for virtual machines.

Find Out if Your Processor Support (Second Level Address Translation) SLAT [Tutorial] YouTube
Second Level Address Translation , also known as nested paging, is a hardware-assisted virtualization technology which makes it possible to avoid the overhead associated with software-managed shadow page tables. AMD has supported SLAT through the Rapid Virtualization Indexing technology since the introduction of its third-generation Opteron processors .

Second Level Address Translation in Windows Server 2012 YouTube
Second level address translation is a capability that can be used by the L1 hypervisor to virtualize physical memory. When in use, certain addresses that would be treated as guest physical addresses (GPAs) are treated as L2 guest physical addresses (L2 GPAs) and translated to GPAs by traversing a set of paging structures. The L1 hypervisor can.

Second Level Address Translation no HyperV TI Especialistas
Second-level address translation is needed for three reasons: to allow the guest view of memory to differ from the physical address map; to protect hypervisor memory and other guests' memory from the guest; and to allow the hypervisor to intercept certain memory and MMIO accesses in order to virtualization the platform and devices.

How can I turn on Second Level Address Translation (SLAT) HP Support Community 7478026
SLAT or Second Level Address Translation is a technology that works with Hyper-V. It is supported by both Intel and AMD processors. It is called Extended Page Table (EPT) in Intel processors and.

Find Out if Your Processor Support (Second Level Address Translation) SLAT [Tutorial] YouTube
Second Level Address Translation is a technology introduced in both Intel and AMD flavors of processors. Both companies call their version of the technology different names, Intel's version is called EPT(Extended Page Tables) and AMD calls theirs RVI (Rapid Virtualization Indexing). Intel introduced Extended Page Tables in its processors that.

EPTbased Second Level Address Translation (the abbreviations R, W, X... Download Scientific
Check this HP Support doc ( Link ), Computer Setup-Security settings for virtualization options. Then enable Windows Hypervisor Platform in Control Panel, Programs and Features, Turn windows features on or off. This should enable SLAT.

PPT Introduction to HyperV PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2386008
The second level of translation maps the GPA space into the SPA space. In order to do this, the Windows hypervisor maintains a shadow page table that combines the two levels of address space translation into a single page table.

How To Find Out if Your Processor Support (Second Level Address Translation) SLAT YouTube
Hyper-V requires Second Level Address Translation (SLAT) -- present in the current generation of 64-bit processors by Intel and AMD. You can run 3 or 4 basic virtual machines on a host that has 4GB of RAM, though you'll need more resources for more virtual machines.

EPTbased Second Level Address Translation (the abbreviations R, W, X... Download Scientific
Learn How Our Global translation, Language and Localization Services Can Work For You. Achieve Your Global Goals. Get Translation for Banking Info to Help You Excel! Contact Us.

EPTbased Second Level Address Translation (the abbreviations R, W, X... Download Scientific
SLAT or Second Level Address Translation, is a technology that was applied on Intel and AMD processors. Intel's SLAT technology is represented as EPT (Extended Page Table). This technology is.

Find Out if Your Processor Support SLAT (Second Level Address Translation) [Tutorial] YouTube
Second Level Address Translation (SLAT) is a hardware mechanism including Extended Page Tables (EPT) or Nested Page Tables supported when Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT-x) is enabled. Go to the product specification page for your processor and look for Intel® Virtualization Technology located under Advanced Technology.
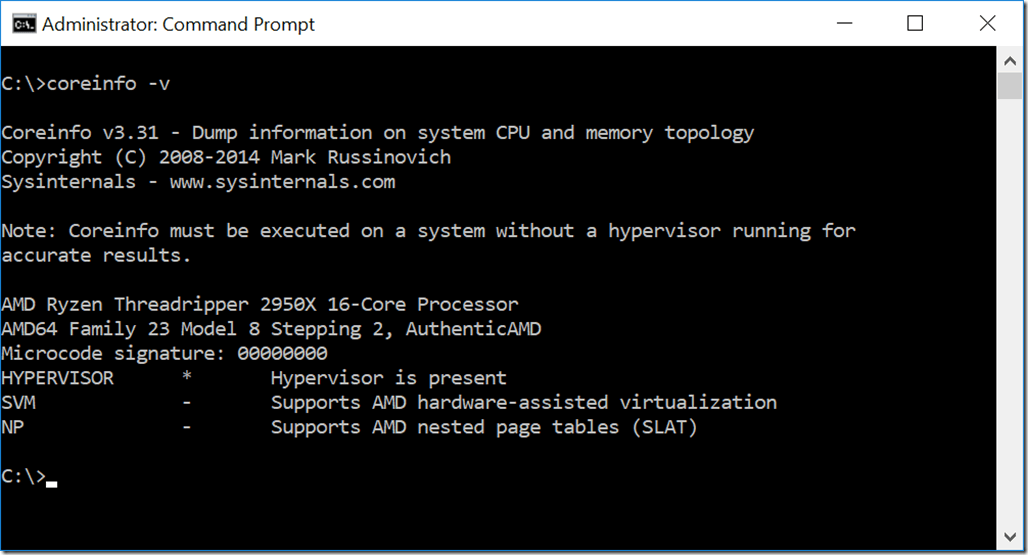
How to Check if Your Processor Supports Second Level Address Translation (SLAT) Glenn Berry
Second Level Address Translation (SLAT) Second Level Address Translation ( SLAT) or nested paging is an extended layer in the paging mechanism used to map hardware-based virtualization virtual addresses into the physical memory.
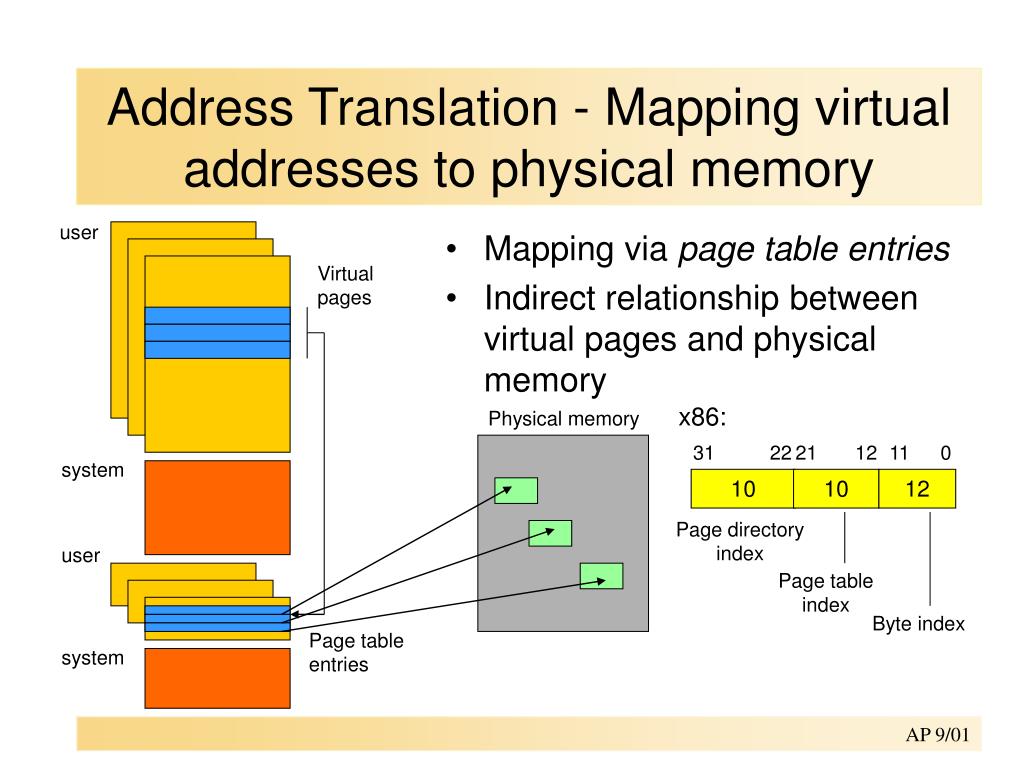
PPT Address Translation Mapping virtual addresses to physical memory PowerPoint Presentation
Other than that, the main difference in hardware is that second-level address translation (SLAT) is now required instead of recommended. For details about maximum supported configurations for Hyper-V, such as the number of running virtual machines, see Plan for Hyper-V scalability in Windows Server 2016.